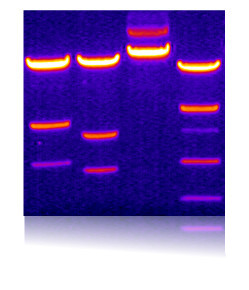
Image of an DNA agarose gel
This site requires JavaScript, please enable it!
Welcome to this site
Molecular cloning is a basic and
very useful method in molecular biology. Cloning allows combining DNA
fragments from different sources into one DNA molecule like a plasmid.
Plasmids can be easily amplified in E. coli. Plasmids can also be used
to express proteins in bacteria and eucariotic cells. Furthermore,
plasmids may be used for instance as p-element vectors for generating
transgene fruit flies.
One application for molecular
cloning is to replace a gene in a plasmid by another gene. Another is
adding multiple functional elements into a plasmid. For instance a
p-element vector does not only have a plasmid backbone and the gene of
interest, but also for tissue specific expression a promoter and a 3’UTR
with a polyadenylation signal, and a p-element for random genomic
integration. Such a plasmid may have some 10 000 base pairs.
Successful cloning requires an appropriate cloning strategy, which is in mathematical terms a
combinatorial problem. A typical application is designing a
preselection digest to reduce the background in the ligation reaction.
Here we provide a free online tool to find fitting enzymes for designing your preselection digests.
Simply give the sequences of the constructs you want to compare, and we
will provide you with a list of all enzymes you can use for your preselection.
Data security:
No sequence data will be uploaded, everything is processed in your local browser with JavaScript.
Introduction
In molecular cloning, restriction enzymes are used to cut out a fragment of DNA from a Donor Vector to
ligate it then into a previously opened Recipient Vector. The DNA fragments are separated on an agarose gel.
However, restriction enzymes may digest incompletely, leaving not only backbone and insert, but also linearized DNA molecules in the reaction.
A linearized plasmid of 10000 bp can be easily separated from a 1000 bp cutout fragment but is difficult to separate from a 9000 bp
backbone fragment. Therefore, even after gel isolation linearized fragments may be left, and used in the ligation.
A single fragment is more likely to be ligated with itself, than two are ligated together. This leads to a high background.
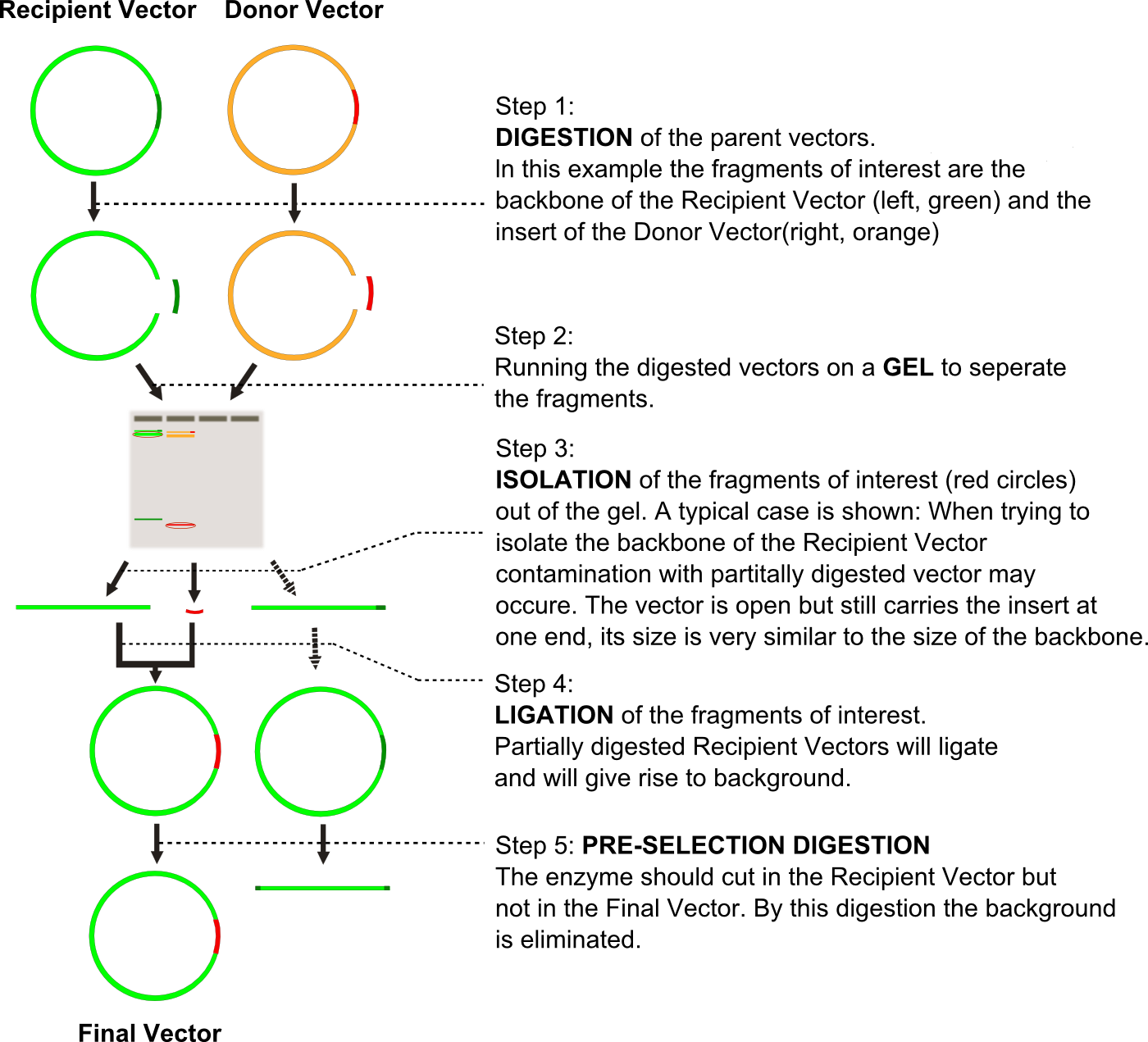
The background can be substantially reduced by a preselection digest. Here another enzyme is used that does not cut the Final Vector after
ligation, but cuts the Recipient Vector. This preselection enzyme cuts after ligation all original Recipient Vectors that have been religated.
The challenge here is finding a preselection enzyme, which is in mathematical terms a combinatorial problem. An easy way to find such enzymes is
provided by preselector.uni-jena.de.
Figure 1: Preselection digests give the opportunity to remove the vectors not wanted for transformation. The vectors are treated with an enzyme that
cuts the Recipient Vector but not the Final Vector. The Recipeint vector is linearized and is unsuitable for transformation
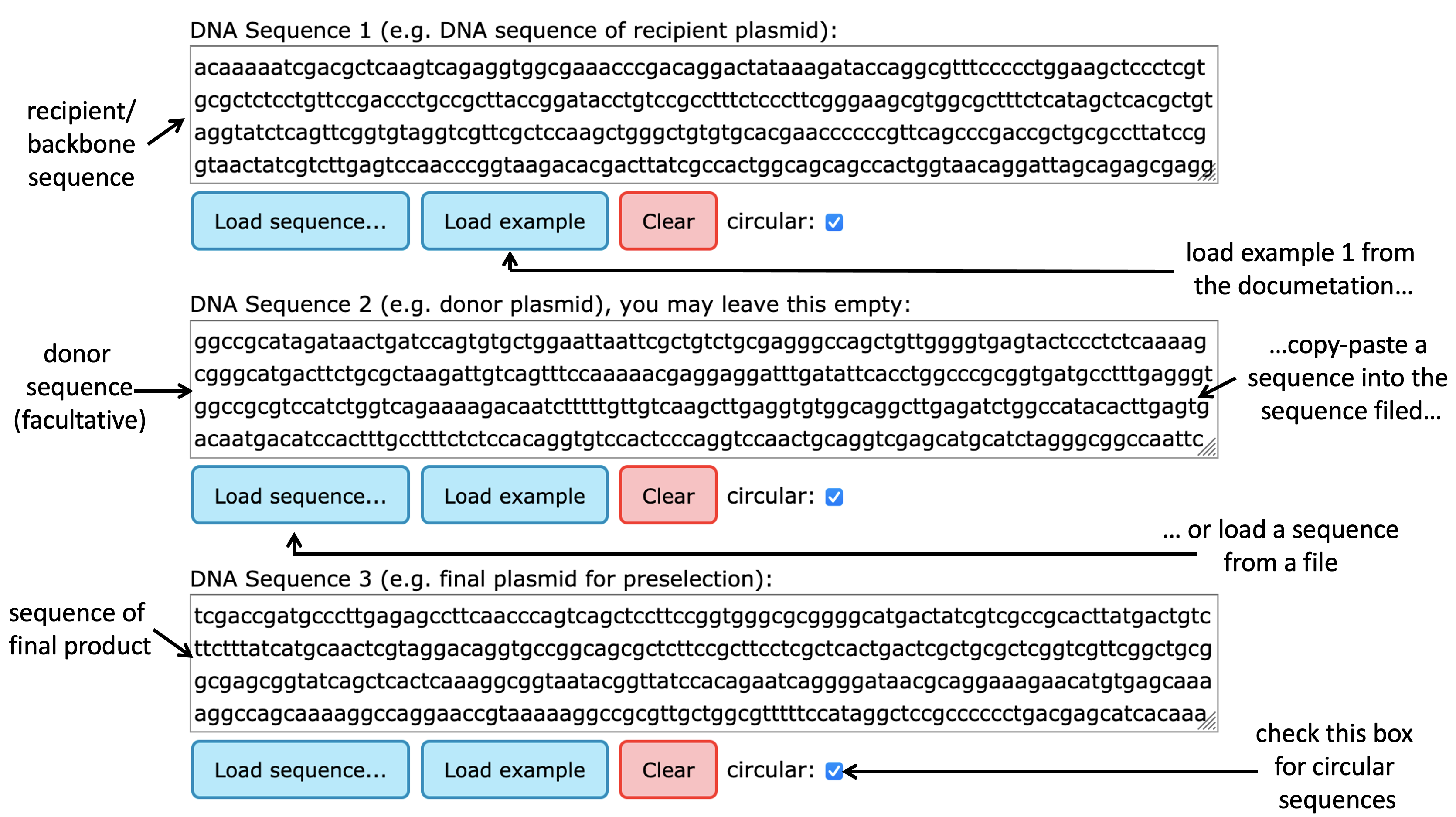
You have to provide your two sequences in plain text. You can copy and paste the sequences into our web form.
In the case of a preselection digest e.g. the sequence of the Recipient Vector, optionally the donor insert, and the sequence of the Final Vector.
An example of a plain text DNA sequence in 5-3 direction:
AGCTAGTCGATGCTATATTTAGCGATGCTAGTCGACTAGCTAAGGCTAGTGATCGAGCTGATCTATCGGATCTAGCGATCGATCGACTAC
What do you get?
You enter two or three DNA sequences, indicate whether they are linear or circular.
And you get for each sequence, a list of cutting and another list of all non-cutting enzymes.
It also displays the enzymes that cut the first but not the third sequence, and the enzymes that
cut the second but not the third sequence. This way you can select your enzymes for your
preselection, i.e. enzymes that cut in the recipient but not in the final plasmid. In addition you get
a list of all non-cutting enzymes for each sequence.
How does it work?
The sequences you provide are processed by a JavaScript program. No sequence is uploaded to the server. All sequences remain in the browser.
The JavaScript program uses regular expressions to search for the recognition sequences of restriction enzymes from the Rebase database.
Disclaimer
For research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic applications.
Literature
About cloning, restriction enzymes, and their application:
Matsumura, I. (2015) Why Johnny can’t clone: Common pitfalls and not so common solutions. BioTechniques, 59, 4-13.
Zeng, Q., Eidsness, M.K., Summers, A.O. (1997) Near-Zero Background Cloning of PCR Products. BioTechniques, 23, 412-418.
Spear, M.A. (2000) Efficient DNA subcloning through selective restriction endonuclease digestion. BioTechniques, 28, 660-668.
Xu, Q., Zhang, D. and Downie, B. (2005) Rapid and Efficient Subcloning of DNA Without Dephosphorylation or Gel Electrophoresis. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology - Part B Molecular Biotechnology, 29, 111-117.
Nathans, D. and Smith, H.O. (1975) Restriction endonucleases in the analysis and restructuring of dna molecules. Annu Rev Biochem, 44, 273-293.
Roberts, R.J., Vincze, T., Posfai, J., Macelis, D. (2015) REBASE-a database for DNA restriction and modification: enzymes, genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res, 43 (Database issue), D298–D299.
About design of plasmid vectors in general:
Tolmachov O. Designing plasmid vectors. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;542:117-29.
About p-vector cloning:
Townson, S.M., Chang, B.S., Salcedo, E., Chadwell, L.V., Pierce, N.E. and Britt, S.G. (1998) Honeybee blue- and ultraviolet-sensitive opsins: cloning, heterologous expression in Drosophila, and physiological characterization. J Neurosci, 18, 2412-2422.
Knox, B.E., Salcedo, E., Mathiesz, K., Schaefer, J. Chou, W.H., Chadwell, L.V., Smith, W.C., Britt, S.G., Barlow, R.B. (2003) Heterologous expression of Limulus rhodopsin. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 278, 40493-40502
Quick Guide
Paste or load from file your DNA sequences into the respective fields, and check the box if your sequence is circular. Sequence 1 may be for instance the sequence of the recipient plasmid, and sequence 3 that of the final plasmid including the insert. Sequence 2 is optional, and can be used that of the donor plasmid. The sequences can be raw or in fasta format and also be quite long since they are not uploaded to the server, but processed in the local browser. If more then one fasta sequence is in one text field then the first one is used and the others are ignored. The sequences should only contain the four canonical bases A, C, G, and T, case is ignored. Characters that are not letters in the English alphabet are ignored. Sequences for instance may come with a base pair index on the start of every new line. If a sequence contains another letter then A, C, G, or T, a warning is displayed below the “Submit and digest” button on submission. We recommend fixing this problem, since Preselector cannot know what do with an ambiguous base such as N. Although preselector is designed for preselection digests, you can also use it to compare restriction enzyme site availability for any other application.
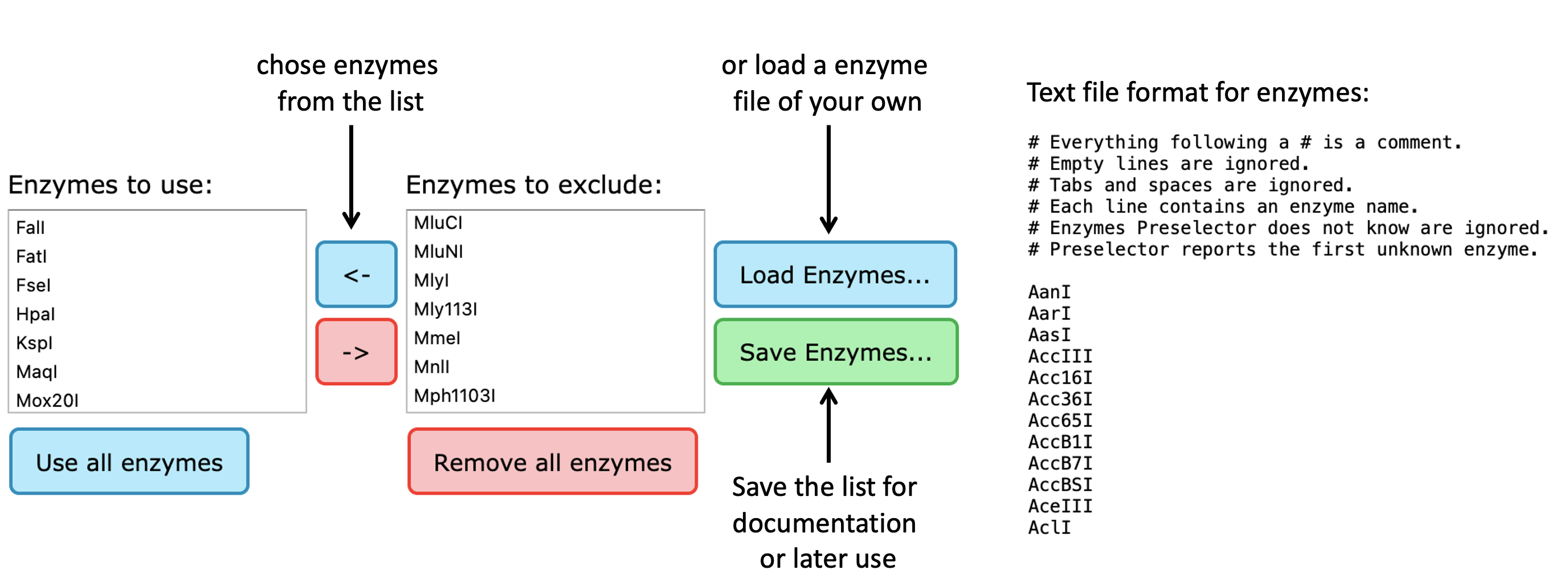
Choose the restriction enzymes you want to use for searching. For instance if you want to exclude some enzymes, select them in the “Enzymes to use” list box and move them with the arrow over to the “Enzyme to exclude” list box. You can use the shift and CTRL (CMD on a Mac) keys to select more than one enzyme at once. Alternatively, you can provide a text file containing the enzymes (format in the right panel). The file should contain one enzyme per row, and unknown enzymes will be ignored. Preselector will warn about the first unknown enzyme, it encounters. You can ignore this warning safely. In addition, you can save the list of enzymes for reuse or documentation.
Click “Submit and Digest” to run the analysis. Preselector checks your inputs for the correct format and issues a warning if any characters other than ‘ATGC’ are detected (arrow in the figure below).
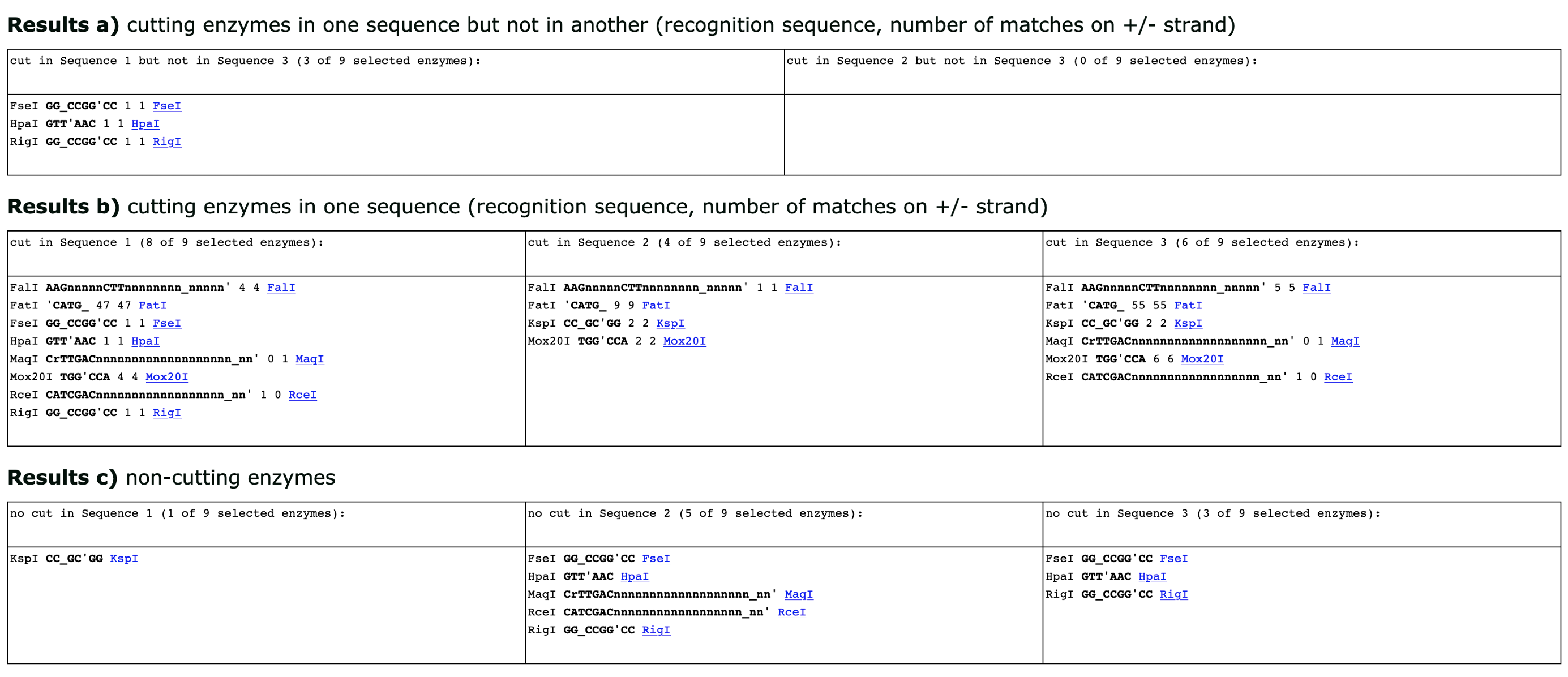
Your results will be displayed in the three tables below: In (a), the enzymes that cut in sequence 1 but not in sequence 3 (recipient and final plasmid, respectively; left column), or sequence 2 but not in sequence 3 (donor and final plasmid, respectively; right column). The two other tables show all the enzymes that cut (b) and all the enzymes enzymes that do not cut (c) provided sequences.
Examples
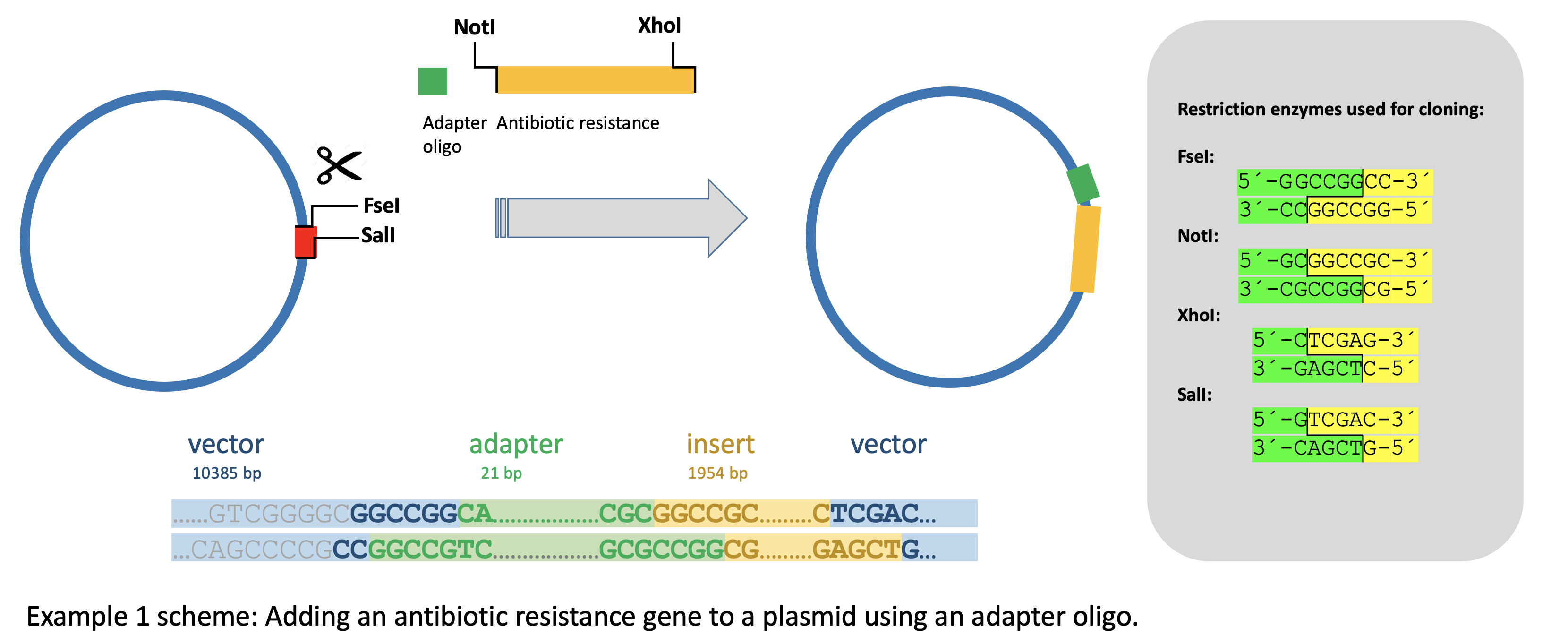
Example 1 - Cloning of a three-fragment plasmid.
This is the example that can be loaded on preselector.uni-jena.de. Here, we cloned a ~2kb insert into a ~10kb recipient plasmid to create a ~12kb final plasmid. The insert had a puromycin resistance and an internal ribosomal entry site (IRES), so that the puromycin resistance was translated from the same transcript as the protein of interest that was already in the recipient plasmid. Therefore, we could not use any multiple cloning site (MCS), there.
We cut out the insert from the donor plasmid with the restriction enzymes NotI and XhoI and opened the backbone with FseI and SalI. Since the overhangs created by NotI and FseI are not compatible, we designed a small adapter fragment with NotI and FseI compatible overhangs. However, now we had three fragments to ligate - insert, adapter, and backbone. This reduces the probability of a complete ligation and leads to background contamination with religated recipient plasmids. Consequently, none of the colonies we analyzed did contain the desired final plasmid but only religated donor recipient plasmids. To not waste more time on screening colonies, we instead decided to use a preselection digest. In this case, we had designed the adapter such that the FseI recognition site was deleted upon ligation, so that we could safely use FseI for this step. As a result, the number of colonies was reduced, but we were able to directly isolate the desired construct from seven out of ten colonies. While designing, we still had to avoid choosing an enzyme that cuts the insert and validate the final plasmid. We did this with preselector.uni-jena.de. It returned four suitable enzymes including the one we used. In other cases of ligating three fragments, it may not be feasible or desirable to delete a restriction enzyme site as described here, making it necessary to find a fitting enzyme first (as described in Example 2).
Sequences:
Sequence 1 (recipient, 10634 bp)
Sequence 2 (insert, 1954 bp)
Sequence 3 (final plasmid, 12352 bp)
Enzymes found by preselector:
Condition
Number of enzymes
Cut sequence 1 but not sequence 3
4
Cut sequence 2 but not sequence 3
0
Cut sequence 1
662
Cut sequence 2
542
Cut sequence 3
696
Cut not sequence 1
886
Cut not sequence 2
206
Cut not sequence 3
52
Enzymes cutting recipient but not final:
Enzyme
Sequence
FseI
GG_CCGG’CC
HpaI
GTT’AAC
KspAI
GTT’AAC
RigI
GG_CCGG’CC
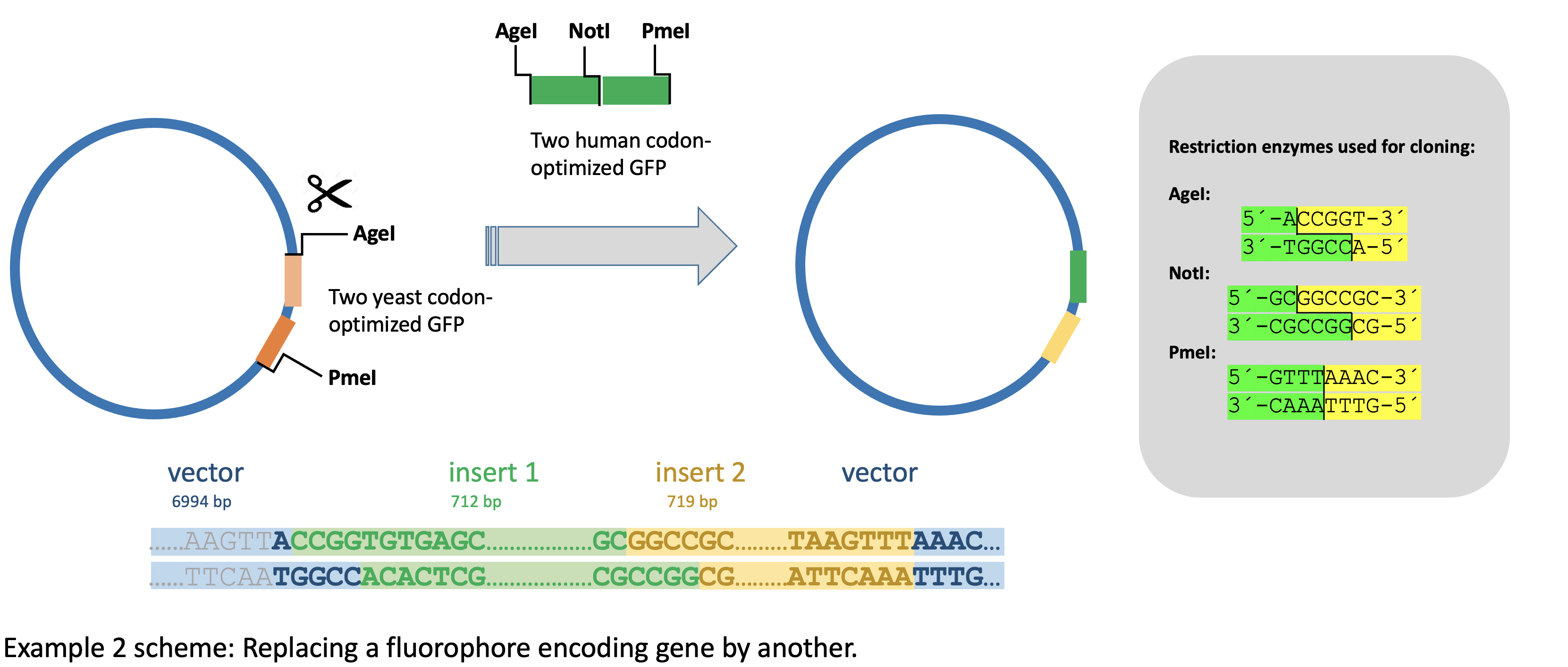
Example 2 - Replacing a fluorophore encoding gene by another.
Here, we replaced the fluorophore in the plasmid pET296-YcpLac111-EF1a-MCP-NLS-2xyeGFP. The plasmid encodes a mRNA-binding MS2-coat protein (MCP), and its sequence is fused to two open reading frames (ORFs) encoding a EGFP for fluorophore-tagging. However, these original ORFs were codon optimized for expression in yeast, whereas we intended to express the construct in human cells. Therefore, we cut out both original EGFP sequences with the restriction enzymes PmeI and AgeI and amplified two human codon optimized EGFP sequences from another plasmid with PCR. We digested the PCR products with the appropriate enzymes and tried to ligate them into the MCP recipient plasmid. However, despite several attempts, we could not get a clone with both human codon optimized EGFP fragments integrated. We therefore decided to use a preselection digest that would cut the original recipient, but not the final plasmid. preselector.uni-jena.de returned twelve enzymes, and we chose MscI. This preselection digest gave less colonies after transformation, but three of four picked colonies contained the desired final plasmid.
Here, we cannot rely on the multiple cloning site (MCS), since the restriction enzyme sites there may also exist in the MCP and EGFP sequence portions, so that we have to check the whole construct.
Sequences:
Sequence 1 (recipient, 8437bp)
Sequence 3 (final plasmid, 8425bp)
Enzymes found by preselector:
Condition
Number of enzymes
Cut sequence 1 but not sequence 3
10
Cut sequence 1
612
Cut sequence 3
630
Cut not sequence 1
136
Cut not sequence 3
118
Enzymes cutting recipient but not final:
Enzyme
Sequence
FauNDI
CA’TA_TG
HauII
TGGCCAnnnnnnnnn_nn’
MlsI
TGG’CCA
MluNI
TGG’CCA
Mox20I
TGG’CCA
MscI
TGG’CCA
Msp20I
TGG’CCA
NdeI
CA’TA_TG
XbaI
T’CTAG_A
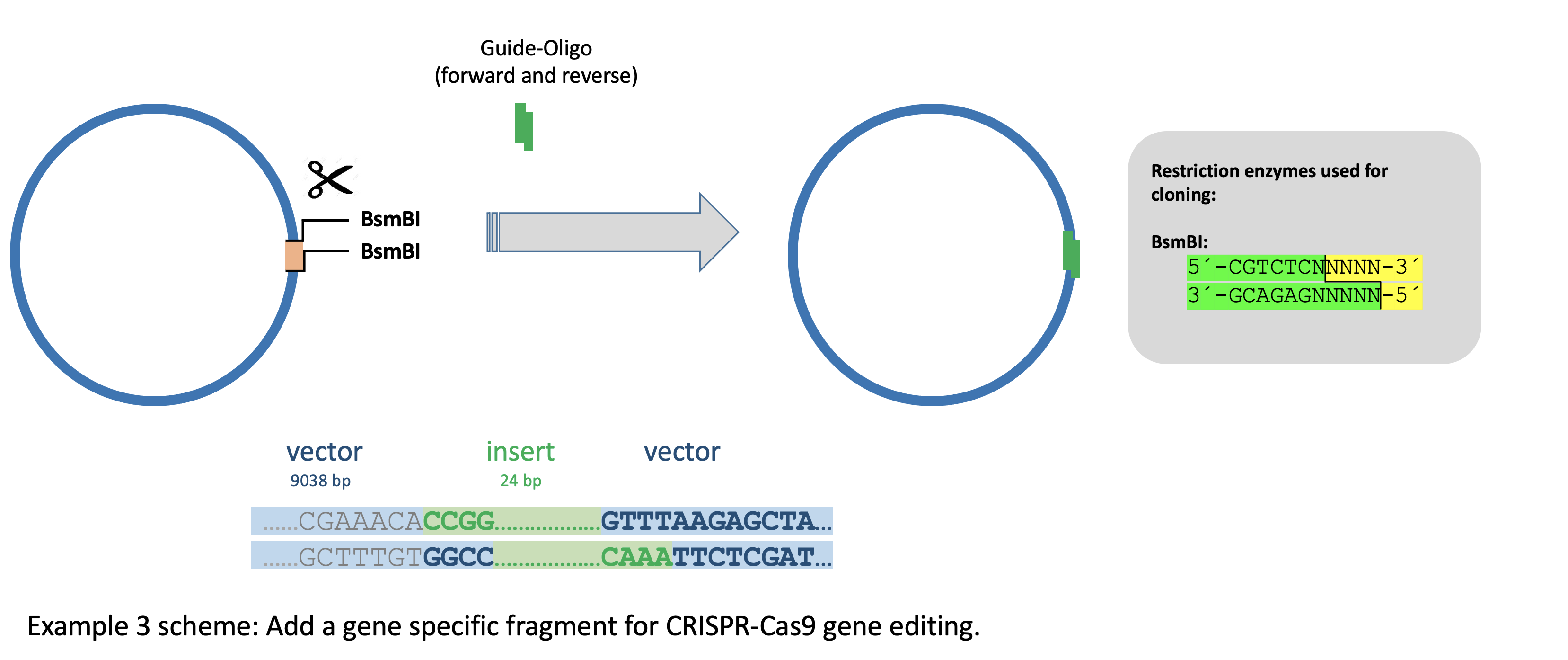
Example 3 - Add a gene specific fragment for CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing.
A cloning step is also typically needed for CRISPR-Cas9 dependent gene editing. The Cas9 enzyme uses a specific guide RNA to recognize a target sequence. Here, we used a backbone containing a fluorescent-tagged Cas9 with a guide RNA, which we completed by inserting a custom oligonucleotide for sequence specificity.
To do that, we opened the backbone at both sites with the restriction enzyme BsmBI. To avoid the laborious and time-consuming task to identify the right colony after transformation, we used a preselection digest. For that, we used BsmBI, which we found with preselector.uni-jena.de among other three restriction enzymes we could use.
It is not hard to imagine a slightly different scenario, in which, depending on the insert, no enzyme exists that cuts the recipient but not the final vector. This would make us double and triple check our search if done manually. However, with preselector.uni-jena.de we can be sure that we either must change our CRISPR target site or that we must use another CRISPR-Cas9 recipient plasmid with a different multiple cloning site.
Sequences:
Sequence 1 (recipient, 9068 bp):
Sequence 3 (final plasmid, 9062 bp):
Enzymes found by preselector:
Condition
Number of enzymes
Cut sequence 1 but not sequence 3
3
Cut sequence 1
672
Cut sequence 3
669
Cut not sequence 1
76
Cut not sequence 3
79
Enzymes cutting recipient but not final:
Enzyme
Sequence
BsmBI
CGTCTCn’nnnn
Esp3I
CGTCTCn’nnnn
PacI
TTA_AT’TAA
Digester for Preselection
DNA Sequence 1 (e.g. DNA sequence of recipient plasmid):
Load sequence...
Load example
Clear
circular:
DNA Sequence 2 (e.g. donor plasmid), you may leave this empty:
Load sequence...
Load example
Clear
circular:
DNA Sequence 3 (e.g. final plasmid for preselection):
Load sequence...
Load example
Clear
circular:
Enzymes to use:
Enzymes to exclude:
<-
->
Load Enzymes...
Use all enzymes
Remove all enzymes
Submit and Digest
Clear Results
Clear All Sequences
Results a) cutting enzymes in one sequence but not in another (recognition sequence, number of matches on +/- strand)
cut in Sequence 1 but not in Sequence 3:
cut in Sequence 2 but not in Sequence 3:
Results b) cutting enzymes in one sequence (recognition sequence, number of matches on +/- strand)
cut in Sequence 1:
cut in Sequence 2:
cut in Seqeunce 3:
Results c) non-cutting enzymes
no cut in Sequence 1:
no cut in Sequence 2:
no cut in Seqeunce 3: